联系我们
竺可桢-南森国际研究中心
邮 箱:[email protected]
邮 编:100029
地 址:北京市朝阳区德胜门外祁家豁子华严里40号 竺南中心

科研进展
Research Progress北极海冰对欧亚春季极端高温事件的影响及预报价值
Influence and prediction value of Arctic sea ice for spring Eurasian extreme heat event
[2022-08-08]
【中文介绍】
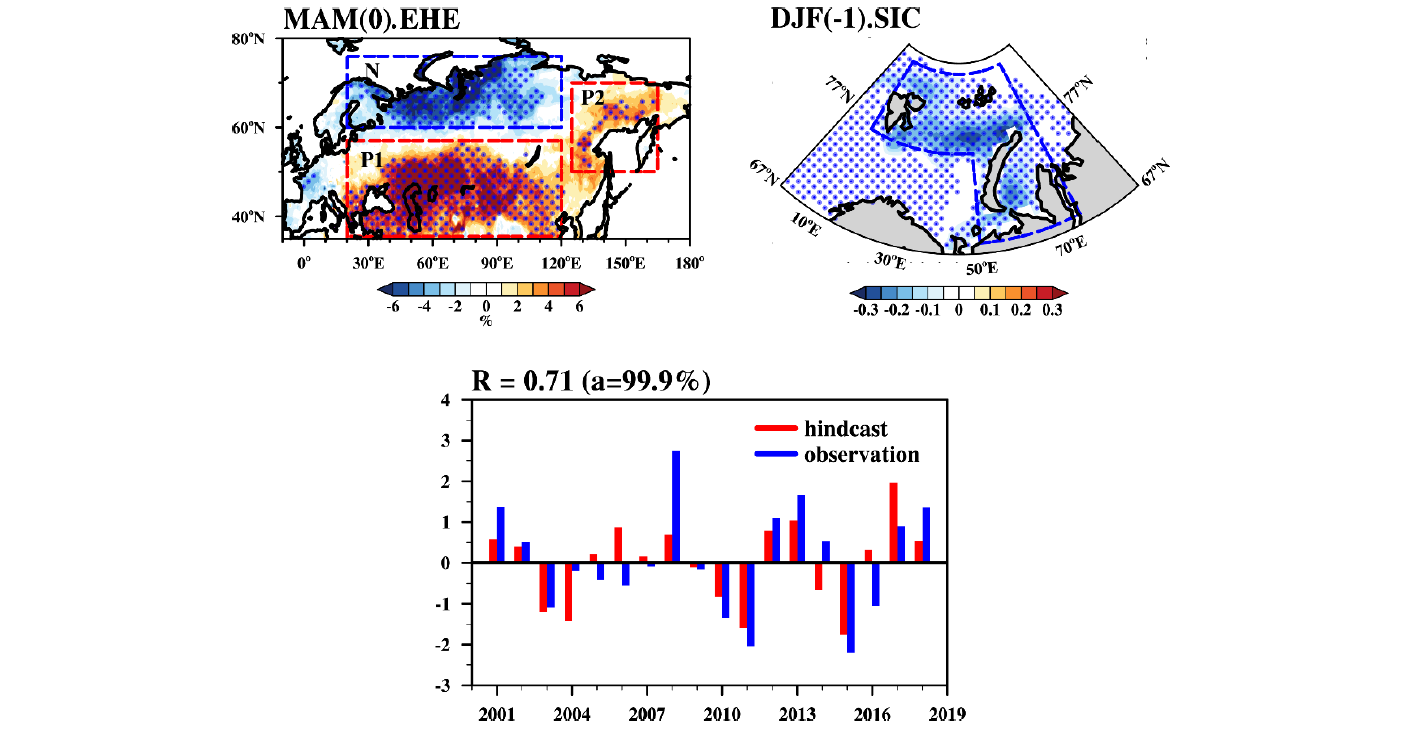
本世纪以来,欧亚地区春季的极端高温事件愈加频发,对生态环境和人体健康等造成了巨大的危害。但目前对欧亚春季极端高温事件变化机制的认识还很薄弱。本文研究揭示出,冬季巴伦支海—喀拉海海冰异常对2000年后欧亚地区春季极端高温事件的年际变化具有重要影响。冬季海冰异常可以通过影响平流层—对流层相互作用,进而导致次年春季欧亚地区对流层大气环流的变化,从而有利于该地区春季极端高温事件呈现出南、北偶极的分布特征。交叉检验结果显示,利用冬季巴伦支海—喀拉海海冰异常预测的欧亚春季极端高温事件偶极模态指数与观测指数的相关系数在2001-2018为0.71,说明上述海海冰异常可以作为春季欧亚地区极端高温事件年际变化的重要预测因子。
【英文介绍】
Since the 21st century, the frequency of spring Eurasian extreme heat events (EHE) has increased, having devastating influence on the ecosystems and human health. In this study, we demonstrate that the winter sea ice anomalies over the Barents-Kara Seas dominate the leading mode of interannual variation of spring extreme heat events over mid-to-high latitude Eurasia in the recent two decades. With faster decline rate and larger variability, the winter sea ice anomalies over the Barents-Kara Seas significantly enhance the troposphere-stratosphere interactions and further exert influence on the spring atmospheric circulations that favor the formation of Eurasian extreme heat events. Cross-validated hindcasts of the dipole mode index of spring extreme heat events using winter sea ice anomalies over the Barents-Kara Seas yield a correlation skill of 0.71 over 2001–2018, suggesting that nearly 50% of its variance could be predicted one season in advance.
【关键图表】
【引用格式】
Sun, J., Liu, S., Cohen, J. et al. Influence and prediction value of Arctic sea ice for spring Eurasian extreme heat events. Commun Earth Environ 3, 172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-022-00503-9